Navigation
Agriculture
World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
Our session will explore “Seeing the unseen: The value of water,” including climate change, ecosystems, sociocultural and economic factors along with how water scarcity, poor water quality and inadequate sanitation negatively impact food security, livelihood choices and educational opportunities for poor families across the world and, in fact, everyone.
Tue, 06/07/2022 - 09:18 — admin
UN Food Systems Summit Receives Over 1,200 Ideas to Help Meet Sustainable Development Goals
On April 1, 2021, the UN Food Systems Summit announced that more than 1,200 ideas and propositions to transform food systems were presented in just six months of public engagement.
Since September, the Summit has hosted regular online meetings, public fora and surveys organised around five priority objectives for more equitable and sustainable food systems.

Tue, 04/06/2021 - 14:36 — admin
Zakaria Ouedraogo of Burkina Faso Produces Film “Nzoue Fiyen: Water Not Drinkable”
For his Internship with Horizon International, an NGO based at Yale University, Zakaria focused on WASH, seeking stories to film from trash polluting city waterways serving as drinking water for local communities to the struggles to find potable water in rural communities. It was this search which lead him to the Ivory Coast.

Thu, 12/05/2019 - 16:29 — admin
"Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
The Authoritative Guide to Water and Sanitation Related Diseases, with Many Revised, Updated and New Chapters, Accompanies the First Edition
Augmenting authoritative interdisciplinary coverage in the first edition, this new edition of Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment expands upon the significance of the changing environment to disease vectors, food systems and nutrition, and population, and the importance of ecosystem health to human health. Many chapters stand as they are in first edition to which readers are referred, and which are not included in this volume.
Thu, 01/31/2019 - 12:22 — admin
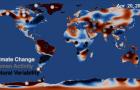
NASA Satellites Reveal Major Shifts in Global Freshwater Updated June 2020
In June 2020, NASA provides an updated report on fresh water availability: "Of all of the water on Earth, 97% is saltwater, leaving a mere 3% as freshwater, approximately 1% of which is readily available for our use. The world’s population is becoming more and more reliant on this precious resource for power, irrigation, industrial practices, and daily consumption." The report is available at: https://earthdata.nasa.gov/learn/toolkits/freshwater-availability
In a first-of-its-kind study, scientists have combined an array of NASA satellite observations of Earth with data on human activities to map locations where freshwater is changing around the globe and to determine why.
The study, published Wednesday in the journal Nature, finds that Earth’s wet land areas are getting wetter and dry areas are getting drier due to a variety of factors, including human water management, climate change and natural cycles.
A team led by Matt Rodell of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, used 14 years of observations from the U.S./German-led Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) spacecraft mission to track global trends in freshwater in 34 regions around the world.
Tue, 05/22/2018 - 14:55 — admin
Meet Freddy the Fly: A New Video Promotes Open Defecation Free Living
Meet Freddy, a fat little fly who loves toilet fondue! Find out what happens to him when the village where he lives is 'triggered' into cleaning up their act to become open defecation free (ODF).Meet Freddy the Fly: A New Video Promotes Open Defecation Free Living

Tue, 06/20/2017 - 10:36 — admin
Soil Nitrogen Age Measurement Could Help Precision Agriculture Scientists Find
Scientists have developed a model to calculate the age of nitrogen in corn and soybean fields, which could lead to improved fertilizer application techniques to promote crop growth while reducing leaching. Nitrogen, a key nutrient for plants, can cause problems when it leaches into water supplies.

Sun, 07/31/2016 - 11:21 — admin
Global Innovation Exchange Co-Created by Horizon International, USAID, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Others
Horizon International co-created the Exchange alongside USAID and organizations from across government, business, academia, and NGOs who believe that together we can tackle humanity’s greatest challenges. The Exchange is providing over 300 summaries of resources from Horizon’s Solutions Site with links to the full articles and case studies and anticipates to soon have over 600 posts from the Solutions Site’s 1,500 plus resources. Explore resources on the Exchange from Horizon International at http://www.globalinnovationexchange.org/resources/organization/3013.

Fri, 06/24/2016 - 11:03 — admin
Climate Change Adaptation Investments Can Help Promote Livelihoods of 65% of Africans According to Report
The report, “Investment in Climate Change Adaptation Can Help Promote Livelihoods of 65% of Africans,” provides a snapshot of current and predicted future impacts of climate change on livelihoods, agriculture, and human and ecosystem health in Africa.

Thu, 08/14/2014 - 14:32 — admin
EnviroAtlas Ecosystem Mapping Tool Launched by US EPA
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on 6 May 2014 released EnviroAtlas, a web-based interactive tool that integrates over 300 separate data layers, helps decision makers understand the implications of planning and policy decisions on our fragile ecosystems and the communities who depend on goods and services from these ecosystems. EnviroAtlas is available to the public and houses a wealth of data and research.

Fri, 05/09/2014 - 11:28 — admin
Search
Latest articles
Agriculture
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
Air Pollution
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
- Global Innovation Exchange Co-Created by Horizon International, USAID, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Others
Biodiversity
- It is time for international mobilization against climate change
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
Desertification
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- UN Food Systems Summit Receives Over 1,200 Ideas to Help Meet Sustainable Development Goals
Endangered Species
- Mangrove Action Project Collaborates to Restore and Preserve Mangrove Ecosystems
- Coral Research in Palau offers a “Glimmer of Hope”
Energy
- Global Innovation Exchange Co-Created by Horizon International, USAID, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Others
- Wildlife Preservation in Southeast Nova Scotia
Exhibits
- Global Innovation Exchange Co-Created by Horizon International, USAID, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Others
- Coral Reefs
Forests
- NASA Satellites Reveal Major Shifts in Global Freshwater Updated June 2020
- Global Innovation Exchange Co-Created by Horizon International, USAID, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Others
Global Climate Change
- It is time for international mobilization against climate change
- It is time for international mobilization against climate change
Global Health
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- More than 400 schoolgirls, family and teachers rescued from Afghanistan by small coalition
Industry
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
- Global Innovation Exchange Co-Created by Horizon International, USAID, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Others
Natural Disaster Relief
- STOP ATTACKS ON HEALTH CARE IN UKRAINE
- Global Innovation Exchange Co-Created by Horizon International, USAID, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Others
News and Special Reports
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- STOP ATTACKS ON HEALTH CARE IN UKRAINE
Oceans, Coral Reefs
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- Mangrove Action Project Collaborates to Restore and Preserve Mangrove Ecosystems
Pollution
- Zakaria Ouedraogo of Burkina Faso Produces Film “Nzoue Fiyen: Water Not Drinkable”
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
Population
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
Public Health
- Honouring the visionary behind India’s sanitation revolution
- Honouring the visionary behind India’s sanitation revolution
Rivers
- World Water Week: Healthy ecosystems essential to human health: from coronavirus to malnutrition Online session Wednesday 24 August 17:00-18:20
- Mangrove Action Project Collaborates to Restore and Preserve Mangrove Ecosystems
Sanitation
- Honouring the visionary behind India’s sanitation revolution
- Honouring the visionary behind India’s sanitation revolution
Toxic Chemicals
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
- Actions to Prevent Polluted Drinking Water in the United States
Transportation
- "Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures" Volume 2 Is Now Available
- Urbanization Provides Opportunities for Transition to a Green Economy, Says New Report
Waste Management
- Honouring the visionary behind India’s sanitation revolution
- Honouring the visionary behind India’s sanitation revolution
Water
- Honouring the visionary behind India’s sanitation revolution
- Honouring the visionary behind India’s sanitation revolution
Water and Sanitation
- Honouring the visionary behind India’s sanitation revolution
- Honouring the visionary behind India’s sanitation revolution

